Priming your painting surface is an essential part of a painting job to obtain a professional finish. As many surfaces can be painted, this article will examine which primer is rated best for wood. As tannin can be an issue in organic surfaces, we will look at the primers frequently used on wooden exterior walls, dry walling, furniture, cabinets, tables, dressers, and other wooden items in your home.
Whenever a newly constructed or manufactured wooden product is painted, there is a chance of the tannin seeping or bleeding through the paint.

What is Tannin
The Oxford Dictionary defines Tannin as “a yellowish or brownish bitter-tasting organic substance present in some galls, barks, and other plant tissues, consisting of derivatives of gallic acid” Tannins help to protect individual plant species from being infected with fungi and bacteria and deter animals from feeding on the plant.
They are comprised of molecules that give them their unique properties and can precipitate and bind plant proteins. The name ‘tannin’ was originally from the term tanning, the process of making leather from animal skins, where tannin was used. Tannin’s molecular weight (mol) ranges from 500 to over 3000.
Types Of Tannin
There are two types of tannins, hydrolyzable tannins, and condensed tannins. A hydrolyzable tannin contains a hydrolyzable core of a carbohydrate called d -glucose. These cores can be partially or completely changed into a chemical compound by the reaction between an acid, such as gallic acid (gallotannins) and alcohol.
Condensed tannins are not susceptible to hydrolysis. All hydrolyzable and some smaller condensed tannins can be dissolved in water Large condensed tannins are not soluble. Although you do not need to be a scientist to choose the correct primer for your paint job, it is advantageous to have a basic knowledge of the properties and types of tannin.
Tannin Bleeding or Seeping
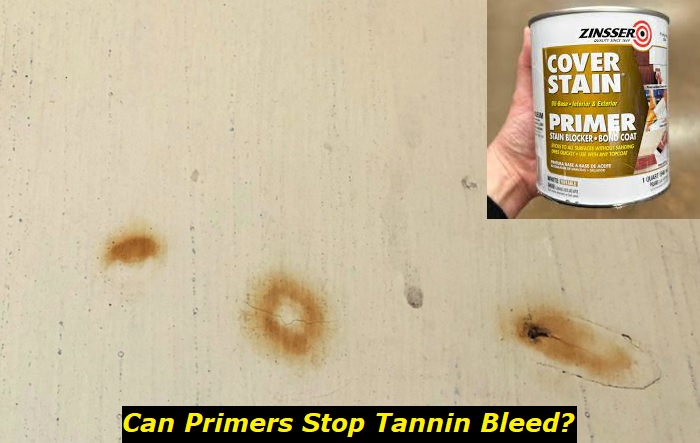
Tannin bleeding or seeping causes a brownish or tan stain on the paint. It can be quite noticeable on white or light-colored surfaces. The discoloration can bleach on exposed surfaces with time but will remain in areas that are damp or receive little sunlight.
Woods such as redwood, cedar, kwila, and beech are prone to bleeding through waterborne paints or stains. Some types of pine and other woods may seep tannin from knots in the wood. When using imported hardwoods, be aware that they may also stain. Unpainted decking wood can cause stain splashes on weatherboards or other surfaces adjacent to the untreated wood.
Staining may occur immediately after painting without a primer or may appear when the surface becomes wet. It is a good idea to test on a less noticeable area, and if you see tannin bleeding occurring, ensure you seal the surface of your project with a good oil-based primer.
Primer Types
The list of primers is about as long as the types of paint you can get. Some common type varieties are:
- Bonding primer e.g. Sika Bonding Primer
- Shellac-based e.g. Zinsser BIN
- General purpose interior e.g. Plascon Multi-Surface Primer
- 3 in-1 primer e.g. VOV Insight Primer 3 in 1
- Oil-based e.g. Diamond Brite Paint 1 Gallon Industrial Oil Base Enamel Primer
- High build e.g. Sherwin-Williams Finish 1 Fp410 High Build 2k HS Primer Gallon Kit
Let’s have a quick look at each one:
Bonding Primer
This primer is best for bonding to difficult surfaces such as tiles and vinyl.
Shellac-Based
Shellac-based primers are tried and tested for a variety of surfaces especially when renovating surfaces that have been treated with other applications. It is the primer of choice for tannin bleeding, stain blocking, water and smoke damage, and seals in odors such as those from smoke.
General Purpose Interior
As the name implies, this primer is formulated for interior surfaces. It is a latex primer that is fast-drying and seals well on surfaces that are textured and porous, providing a single smooth surface for painting and decorating. It can be top-coated with latex or oil-based paint after an hour of drying.
3 in 1 Primer
These products combine the functions of primer, sealer, and undercoat in one application. It provides maximum adhesion, and blocks tannin and other stains, leaving a good surface for topcoats.
Oil-Based
These primers are ideal for bare wood, interior and exterior use. They seal porous surfaces and leave them ready for coats of paint. They prevent tannin bleeds from woods such as cedar and redwood.
High Build Primer
‘High build’ refers to a primer that can be mixed with thinners in various ratios to provide coatings of different thicknesses. It is best used under a color coat of paint.
So, What is the Best Primer to Prevent Tannin Bleed?
Barring personal preferences, most painters prefer shellac or oil-based primers to prevent tannin bleed. Whether you use white or clear, depends on your choice of top paint, varnish, or lacquer. White primer provides a strong, smooth canvas for painting or decorating, whereas, clear is ideal for when you want to preserve the color of the natural wood or wood stain you are using.
Both shellac and some oil primers come from natural sources. Whereas others are synthetic.
Shellac
Shellac is a resin secreted by the female lac beetle. It has been used for centuries as a primer on numerous surfaces such as wood, metal, glass, and ceramic tiles. It is superior for sealing in odors caused by smoke or dampness.
Shellac primers are very fast drying and can be used with oil and latex paints. On the downside, they are not as versatile as oil or latex and emit more fumes. They do not require a rough surface to adhere to, being extremely adhesive and fast drying.
Oil-Based
Oil-based primers are very good for blocking and sealing water-soluble stains and exceptional for blocking tannin. Variant bases may be natural i.e. Linseed oil, or synthetic i.e. Alkyd. This type of primer is used more for interior wooden surfaces such as doors, cupboards cabinet doors, and furniture.
The oil prevents the paint from bubbling from water damage and seals the wood grains. Be aware, however, that oil-based primers contain a larger number of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which are not good for your respiratory health. Make sure you wear a mask when working with it, and allow it to dry completely before breathing in these fumes for a prolonged period.
Conclusion
Tannin bleed or seepage can be a problem for painting wood due to the naturally occurring substances that protect plants while alive. Most tannins can be dissolved in water, except those with large molecules. Tannin bleed can leave paint unsightly with brown or tan-colored stains. With so many primers to choose from, it is not always easy to choose the most suitable one for your paint job.
After a review of the different types of primer, it seems that most painters prefer shellac or oil-based to prevent or mitigate tannin bleeding and other stains. Oil-based is a good alternative on virgin wood to prevent the seeping in the first place, whereas shellac primers are superior when renovating older wood that already has signs of wear, tear, odors, and staining as a cover-up before painting.
- Can You Unmix Paint: Techniques, Consequences, Alternatives - February 23, 2024
- Does Primer Need to be Mixed? Effective Primer Application - February 22, 2024
- How to Make Old Paint Usable Again: Retrieving and Preserving Paint - February 21, 2024